The working principle of the magnetic fuel saver
The magnetic fuel saver is a device that is designed to improve the fuel efficiency of a combustion engine. The device is attached to the fuel line of the engine and uses magnetic fields to improve the atomization and combustion of the fuel. In turn, this results in better fuel economy and reduced emissions from the engine.
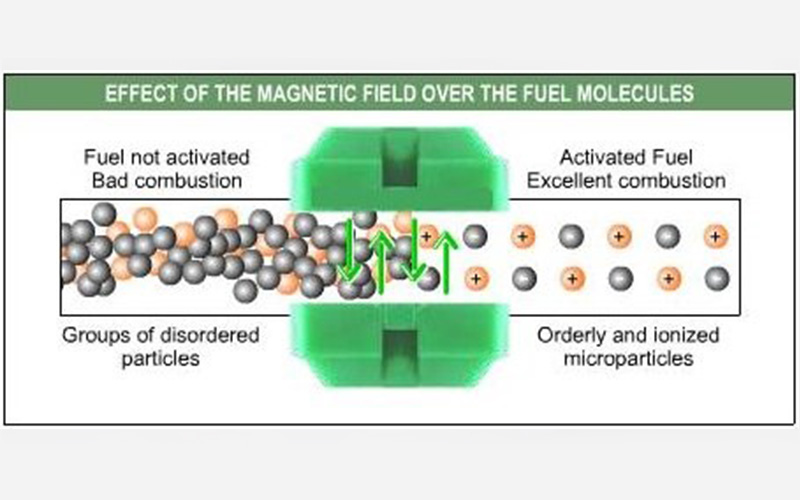
The working principle of the magnetic fuel saver is based on the idea that the magnetic field can alter the structure of fuel molecules, making them more volatile and easier to ignite. This effect is achieved by aligning the molecules of the fuel with the magnetic field, which makes them more uniformly distributed and less prone to clump together.
To understand how this concept works in practice, we need to look at the chemistry of combustion engines. In a typical combustion engine, fuel is mixed with air in the combustion chamber, and then ignited by a spark or compression. The resulting reaction releases energy, which is converted into mechanical work that drives the vehicle.
However, the efficiency of this process is limited by several factors, including incomplete combustion of the fuel, pressure losses during combustion, and heat losses to the engine block. These inefficiencies result in wasted energy that is not converted into useful work.
The magnetic fuel saver aims to address these inefficiencies by modifying the structure of the fuel molecules before they enter the combustion chamber. The device consists of a series of neodymium magnets that are arranged in a specific configuration around the fuel line. When fuel flows through this magnetic field, its molecular structure is altered, making it more volatile and easier to ignite.
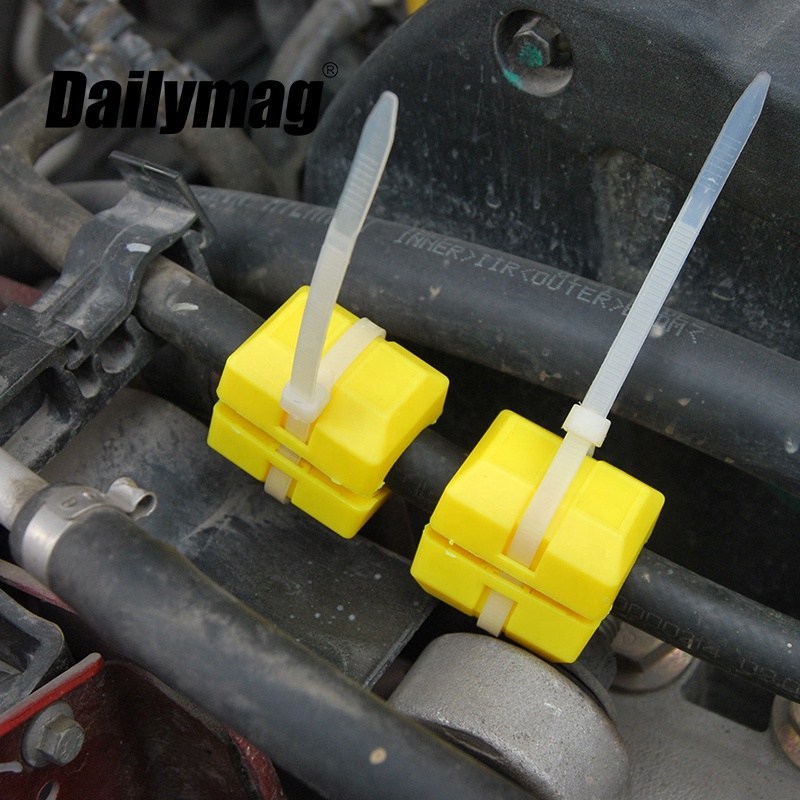

This effect is achieved by causing the hydrocarbon chains in the fuel to align with the magnetic field. Hydrocarbon chains are the basic building blocks of fuel molecules, and consist of a series of carbon and hydrogen atoms bonded together. The alignment of these chains in the magnetic field causes them to become more uniformly distributed and less susceptible to clustering together. This, in turn, makes the fuel more responsive to combustion.
Another way in which the magnetic fuel saver improves combustion is by reducing the surface tension of the fuel. Surface tension is the force that holds the surface of a liquid together, and is caused by the attraction between the molecules at the surface. When the surface tension is high, it can prevent the fuel from dispersing evenly in the combustion chamber, resulting in incomplete combustion and wasted energy.
The magnetic field generated by the magnetic fuel saver reduces the surface tension of the fuel, which allows it to disperse more evenly in the combustion chamber. This results in more complete combustion, which in turn increases the energy output of the engine.
In addition to improving combustion efficiency, the magnetic fuel saver also has several other benefits for the engine. For example, it can help to reduce the accumulation of carbon deposits in the engine, which can clog up the fuel injectors and diminish performance. By improving the atomization of the fuel, the magnetic fuel saver can also reduce the emissions of harmful pollutants such as carbon monoxide and particulate matter.
Overall, the magnetic fuel saver is a simple yet effective device that can help to improve the fuel efficiency and performance of gasoline or diesel engines. By altering the structure of the fuel molecules before combustion, the device can reduce wasted energy and increase the energy output of the engine. While the exact mechanisms of the device are still being studied, there is ample evidence to suggest that it can provide tangible benefits for vehicle owners, and help to reduce the impact of transportation on the environment.